Ⅰ. What is Die Casting?
Die casting is a manufacturing process used to produce metal parts with high precision and intricate details. It is done by injecting molten metal into a place called a mold under high pressure. The molten metal rapidly solidifies to conform to the shape of the mold, and then the final part is removed from the mold. Die casting is typically used to mass produce metal parts with consistent quality and dimensional accuracy.
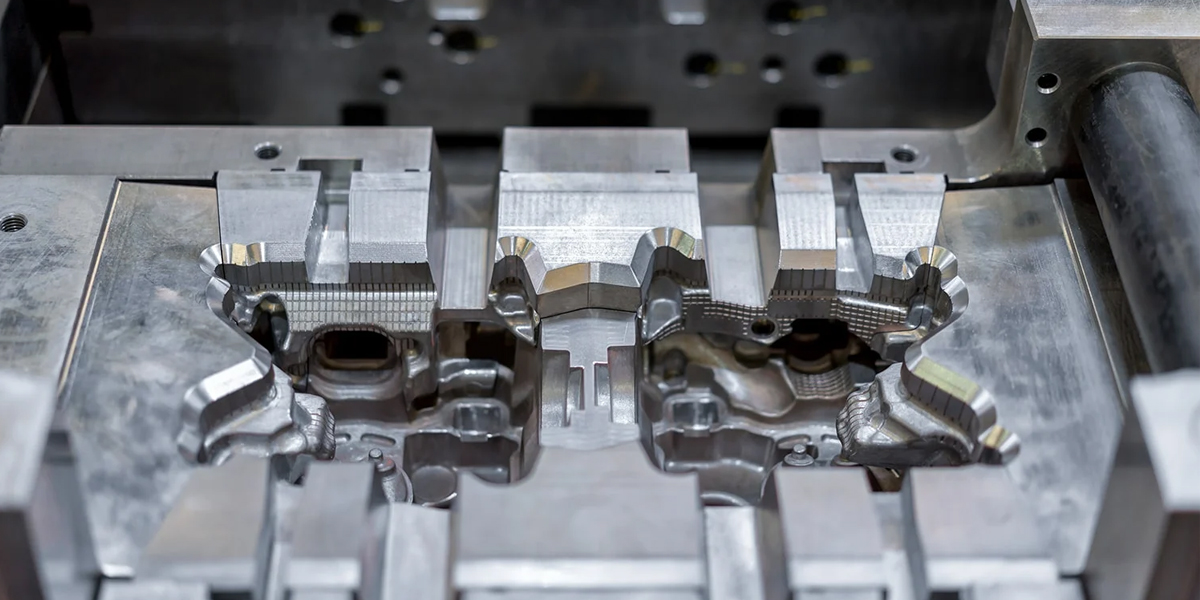
Ⅱ. How does die casting work?
Die preparation: The die casting process begins with the preparation of the die, which consists of two parts, the "mold" and the "cover die". The dies are usually made of hardened steel and are precisely machined to form the desired shape of the final part. They are designed to withstand the heat and pressure of the machining process.
Die Clamping: The two halves of the die are firmly clamped together to form a sealed cavity. This ensures that the molten metal can be injected into the mold under pressure without leakage.
Injection: The molten metal, usually an alloy of aluminum, zinc, magnesium or copper, is melted in a furnace and then injected into the mold cavity. The injection system usually includes a plunger or a hydraulic piston that injects the molten metal into the mold at high speed and pressure. This pressure helps fill the mold quickly and ensures that the molten metal reaches all the intricate details of the mold.
Cooling and Solidification: Once the mold is filled, the molten metal rapidly cools and solidifies within the mold cavity. Cooling channels or water jackets within the mold help extract heat from the molten metal and promote rapid solidification. The solidification time depends on the metal being cast and the design of the part.
Mold opening and ejection: After the metal has solidified and cooled sufficiently, the mold is opened. The two halves of the mold are separated to expose the finished part inside the mold cavity. An ejector mechanism, such as an ejector pin or ejector plate, is used to push or remove the part from the mold. The part is then removed from the mold for further machining and finishing.
Trimming and Finishing: Castings may be trimmed or second machined to remove any excess material, smooth out rough edges, and achieve the desired finish. This may involve removing any excess flying edges, excess material that seeped out of the mold during the injection process, and performing any necessary machining, drilling, or surface preparation.
Recycling and Reuse: Once the part is ejected, any excess or leftover material from the casting process, such as runners and gates, is typically recycled and reused in subsequent casting cycles to minimize waste.
//.Available materials for die-casting
Aluminum alloys:
Aluminum alloys have good fluidity and strength, and are often used in die-casting, especially for manufacturing lightweight parts and complex shapes.
Magnesium alloy:
Magnesium alloy has low density and good mechanical properties, suitable for manufacturing lightweight parts, such as automotive parts and electronic equipment housing.
Zinc alloy:
Zinc alloy has good fluidity and corrosion resistance, commonly used in the manufacture of small parts, decorative items and die-casting molds.
Copper alloys:
Copper alloys have excellent thermal and electrical conductivity and are suitable for the manufacture of parts requiring high thermal and electrical conductivity, such as radiators and electrical components.
Cast iron:
Cast iron is an alloy with high carbon content, good wear resistance and strength, suitable for manufacturing heavy parts, such as automotive engine parts and construction machinery.
Steel alloys:
Certain types of steel alloys are available for die-casting, and these alloys typically have high strength and heat resistance and are suitable for making parts that require higher strength and heat resistance.
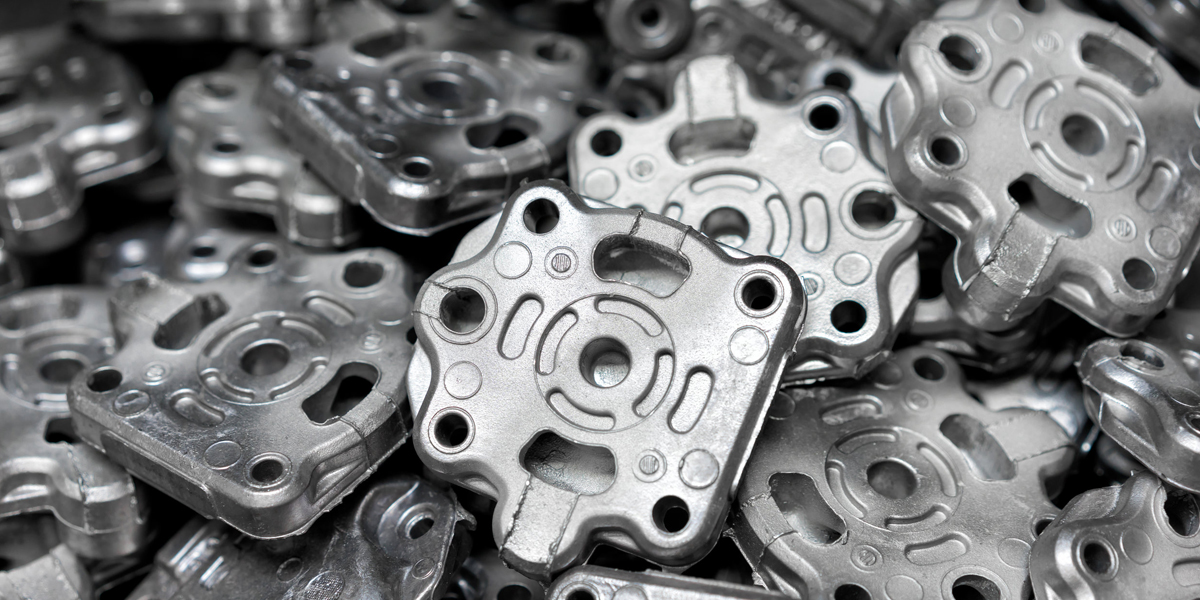

Ⅲ. Applications of Die Casting
Die casting is widely used in the automotive industry to manufacture components such as engine blocks, transmission cases, cylinder heads, intake manifolds and suspension components. The high strength, durability and dimensional accuracy of die castings make them suitable for automotive applications.
Die casting is used in the aerospace industry to produce lightweight and well-constructed components. Examples include aircraft engine components, structural components and housings for avionics. Die castings have a high strength-to-weight ratio, which is critical for aerospace applications.
Electronics and electrical industry:
Many electronic and electrical devices rely on die-cast components for their housings. These include computer components, smartphones, tablets, audio/video equipment, power tools and electrical connectors. Die casting provides the necessary precision, durability and electromagnetic shielding properties required for these applications.
Consumer Products:
Die casting plays a role in the production of a variety of consumer products, including appliances, home fixtures, furniture hardware and sporting goods. The process allows for efficient mass production of high quality parts with complex designs and fine surface finishes.
Die casting is used in the manufacture of medical equipment and devices such as surgical instruments, imaging devices, dental instruments and prosthetics. The ability to produce complex, lightweight and sterile parts makes die casting suitable for medical applications.
Industrial equipment:
Die casting is used to produce industrial machinery and equipment components. This includes components for pumps, valves, compressors, hydraulic systems and machine tools. Die cast components provide the necessary strength, dimensional accuracy and resistance to harsh operating conditions.
Furniture and Lighting:
Die casting is commonly used in the furniture and lighting industries to manufacture decorative parts, handles, hinges and fixtures. This process allows for intricate and aesthetically pleasing designs while maintaining structural integrity.
Energy and Power Generation:
Die casting is used in the energy and power generation sectors to produce components such as turbine blades, heat sinks, motor housings and electrical connectors. The high thermal conductivity and mechanical strength of die castings make them suitable for these demanding environments.
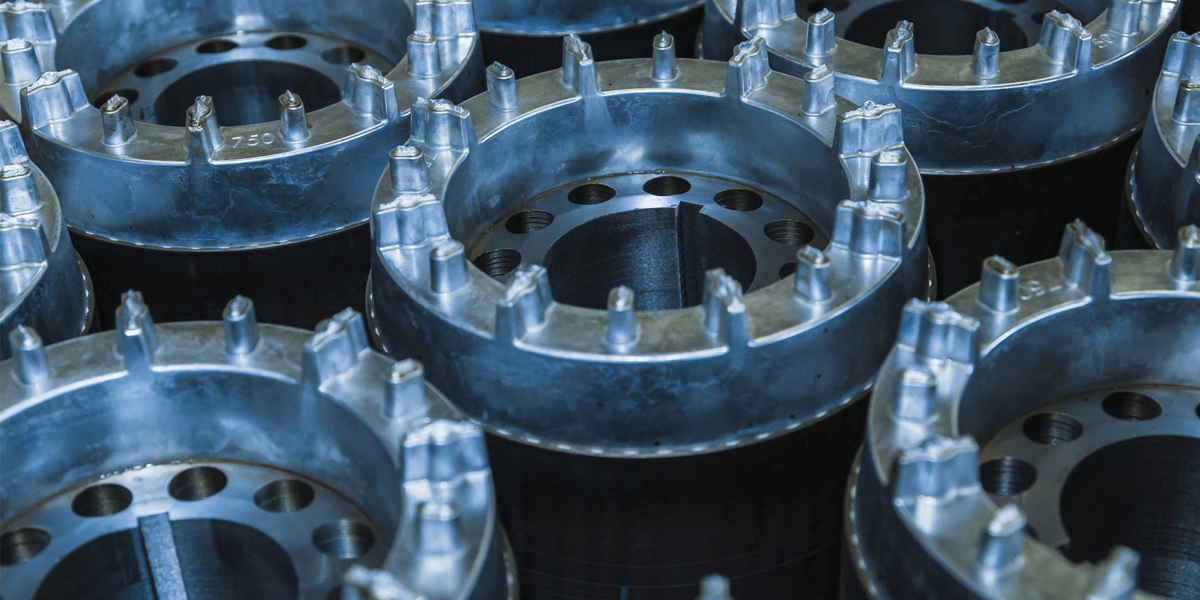
Pros of Die Casting
High precision and dimensional accuracy:
Die casting enables the production of complex shapes with high precision and dimensional accuracy. The dies used in this process have tight tolerances, allowing the part to meet strict specifications.
Superior surface finish:
Die castings often have a smooth and aesthetically pleasing surface finish. The quality of the die surface is directly transferred to the final product, reducing the need for additional finishing operations.
Fast Production Cycles:
Die casting is known for its high production rates. The process allows for rapid injection and solidification of molten metal, resulting in fast cycle times and high volume production.
Strength and durability:
Die cast parts exhibit excellent mechanical properties, including high strength, rigidity and durability. The use of alloys further enhances the structural integrity of the part, making it suitable for demanding applications.
Cost-effectiveness for high-volume production:
Die casting is cost-effective for high-volume production due to its high productivity and efficiency. The ability to create complex shapes in a single operation reduces the need for secondary machining, resulting in lower production costs.
Design flexibility:
Die casting provides the design flexibility to produce complex and detailed parts. It can integrate features such as thin walls, complex geometries and internal cavities that are difficult to achieve with other manufacturing processes.
Cons of Die Casting:
High initial tooling costs:
Die casting requires the fabrication of specialized tooling, which can be costly to design and manufacture. Tooling costs are an important consideration. Die casting is not the best choice for small scale production or when frequent design changes are expected.
Limited Material Selection:
Die casting is primarily suitable for non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, zinc, magnesium and copper-based alloys. Due to its higher melting temperatures and associated challenges, the process is not suitable for ferrous metals.
Part size limitations:
Die casting is typically used to produce small to medium sized parts. Part size and weight are limited by the capacity and capability of the die casting equipment.
Porosity and shrinkage:
The rapid cooling and solidification of molten metal in die casting can sometimes result in porosity and shrinkage defects in the casting. Proper design, gating and process control are necessary to reduce these problems.
Limited repairability:
Once a die casting is produced, modifying or repairing it can be a challenge and costly. Modifications to tools or molds may be required, which can disrupt production and incur additional costs.
Environmental Considerations:
Die casting involves the use of high temperatures and the generation of metal scrap and waste. Proper waste management and recycling practices are critical to reducing environmental impact.
Choosing a good service provider for your Die Casting project is critical to ensuring the quality of your product.
A good service provider will have high quality equipments and use the best materials to produce accurate, durable and high resolution products.
Good customer service and support ensures that you have a smooth and hassle-free experience throughout the project.
Access to a wide range of materials and technologies ensures that your project can be production in the most suitable material and technology for your needs.
Range of services including design assistance, prototyping and production runs.
Cost-effective solutions to meet the needs of your project without compromising quality.
Expertise and experience to provide guidance on design, materials and techniques to ensure the best results.
Fast turnaround times ensure that your project is delivered on time and within budget.
Get an instant quote for your die casting project now