Injection molding is a manufacturing process used to produce parts and products by injecting molten material into a mold. The molten material is usually a thermoplastic or thermosetting polymer that is melted and injected into a mold under high pressure. The mold is then cooled, and the material solidifies, taking the shape of the mold cavity.
Injection molding is a highly versatile process that can be used to produce a wide range of products, from small parts like bottle caps and automotive components to large parts like plastic pallets and toys due to its efficiency, high production rates, and the ability to produce complex shapes with high accuracy and consistency.
Injection molding machines vary in size and complexity, ranging from small desktop machines for prototyping to large industrial machines for mass production. The process is used in a variety of industries, including automotive, aerospace, medical, consumer products, and more.
Injection molding is used in a variety of industries, including automotive, medical, aerospace, and consumer goods. It is often used to produce components such as housings, gears, and enclosures, as well as larger parts like automobile bumpers and dashboards.
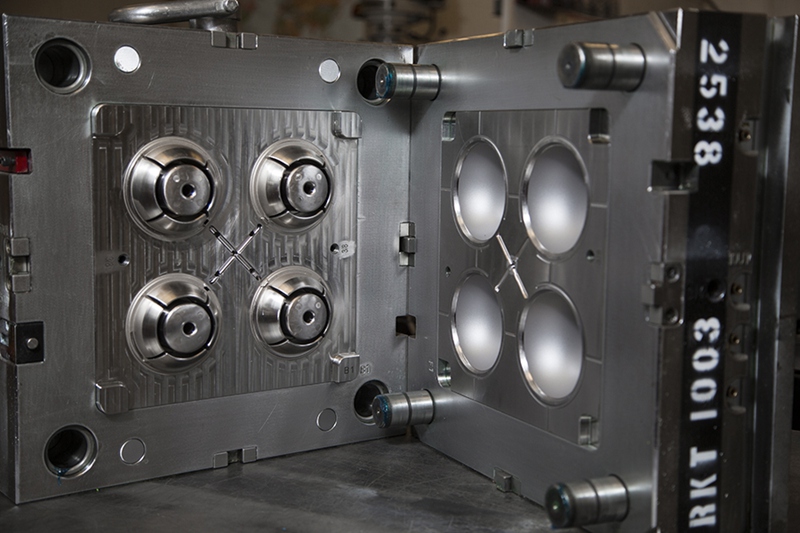
Advantage of injection molding
Injection molding has several advantages over other manufacturing processes. Some of the key advantages of injection molding include:
High production rates: Injection molding is a highly automated process that can produce parts at high volumes and with high efficiency.
Low labor costs: Injection molding requires minimal labor, which makes it a cost-effective manufacturing process.
Consistency and repeatability: Injection molding allows for precise control of the molding process, which results in consistent and repeatable parts.
Versatility: Injection molding can be used to produce parts of different sizes, shapes, and complexities, which makes it a versatile manufacturing process.
Material options: Injection molding can be used with a wide range of materials, including thermoplastics, thermosets, and elastomers.
Reduced waste: Injection molding produces very little waste, as excess material can be easily re-used or recycled.
Surface finish and detail: Injection molding can produce parts with excellent surface finish and detail, making it ideal for applications that require high-quality and precision parts.
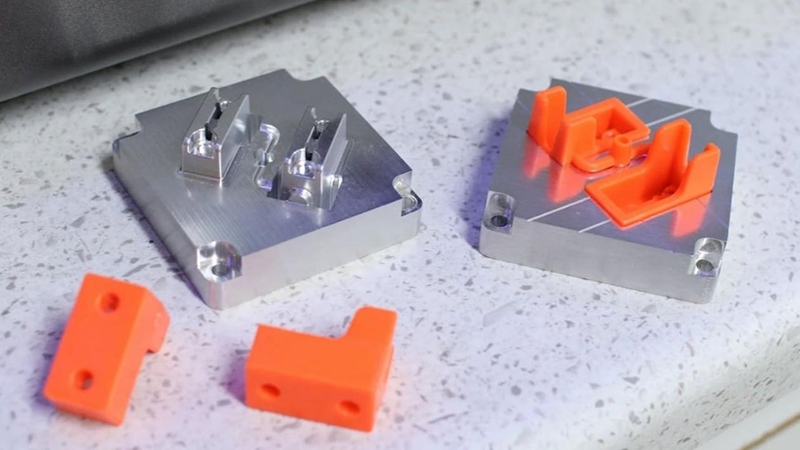
Application of injection molding
Common applications of injection molding include:
Automotive industry: Injection molding is extensively used to manufacture automotive components like bumpers, dashboards, interior trims, and other parts that require high strength and durability.

Consumer goods: Many consumer goods like containers, toys, electronic casings, and household appliances are made using injection molding due to its high accuracy, low cost, and fast production rate.
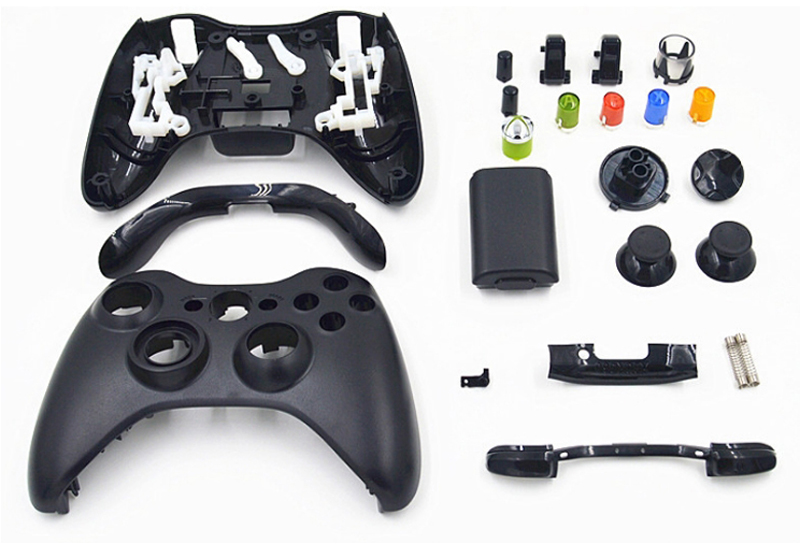

Medical devices: Injection molding is used to produce medical equipment like syringes, IV tubes, and medical devices that require precise dimensions and high purity.
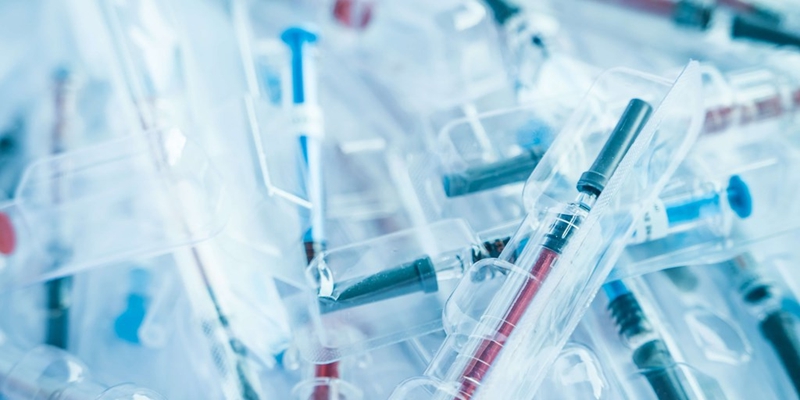
Aerospace industry: Injection molding is used to create lightweight and high-strength components for aircraft and spacecraft, including parts such as seats, ventilation systems, and structural components.

Different between injection molding and die casting
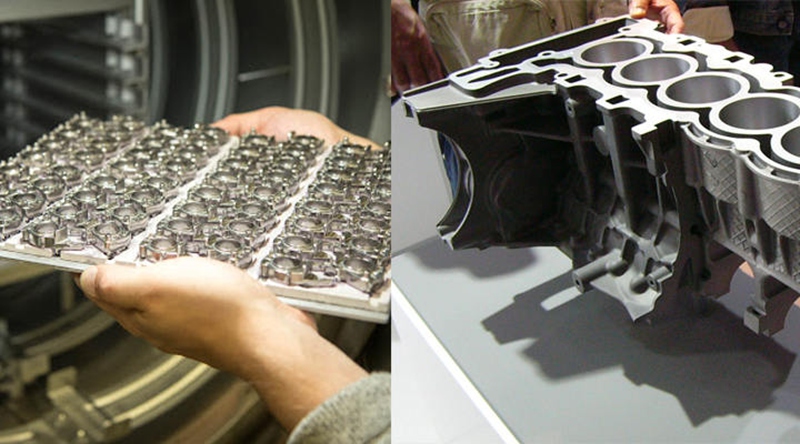

Injection molding and die casting are both manufacturing processes used to produce parts and products from molten material. However, there are several key differences between the two processes:
Material: Injection molding is typically used with thermoplastics, while die casting is used with metals, such as aluminum, zinc, and magnesium.
Molds: Injection molding uses a single, two-part mold that is opened and closed by the injection molding machine. Die casting uses a multi-part mold that is mounted on a die casting machine and opens and closes vertically.
Pressure: Injection molding uses high pressure to inject molten plastic into the mold, while die casting uses even higher pressure to inject molten metal into the mold.
Surface finish: Injection molding can produce parts with a smooth surface finish, while die casting parts have a textured surface finish due to the casting process.
Complexity: Injection molding is better suited for complex parts with thin walls and intricate geometries, while die casting is better suited for parts with thicker walls and simpler geometries.
Cost: Injection molding tends to have lower tooling costs than die casting, but higher production costs due to the use of plastic material. Die casting tends to have higher tooling costs, but lower production costs due to the use of metal material.
Capabilities Of GD-HUB Injection Molding Service
GD-HUB custom injection molding services for plastic prototypes and on-demand production parts. You can get a free injection molding quotation and design feedback within hours.
Minimum order quantities
Rapid Tooling Production as fast as 2 weeks
ISO 9001:2015 certified
24H/7d engineering support
Leading quality inspection and testing
Fast Lead Time