Aluminium Extrusion Overview
Aluminum extrusion is a manufacturing process that involves shaping aluminum alloys into a wide range of cross-sectional profiles. This process is commonly used to create various products and components across industries due to aluminum's desirable properties, such as its lightweight nature, corrosion resistance, and excellent conductivity.
Raw Materials: Aluminum extrusion primarily uses aluminum alloys. These alloys are typically a combination of aluminum, along with other elements such as copper, silicon, magnesium, and zinc. The specific alloy chosen depends on the desired properties of the final product.
Billet Preparation: The process begins with a cylindrical aluminum billet, which is typically heated to a specific temperature to make it more malleable. This preheating helps in the extrusion process by reducing the force required for shaping the aluminum.
Extrusion: The heated billet is placed in a container called a "container" or "container die." The container is located at one end of a hydraulic or mechanical press. A steel tool, known as a "die," is situated at the opposite end of the press. The die contains the desired cross-sectional shape of the final product.
Pressing: The hydraulic or mechanical press forces the heated billet through the die, creating the desired shape. The extrusion process is continuous, and the aluminum emerges from the die as a long, uniform profile. The shape of the die determines the shape of the extruded aluminum.
Cooling: As the aluminum emerges from the die, it is cooled using air or water to set its shape and hardness.
Cutting: After cooling, the extruded aluminum is cut to the desired lengths. This can be done using saws or other cutting methods.
Aging and Heat Treatment: Depending on the alloy used and the desired properties of the final product, the extruded aluminum may undergo aging or heat treatment processes to further enhance its mechanical properties.
Surface Finish: The extruded aluminum profiles may undergo various finishing processes, such as anodizing, powder coating, painting, or polishing, to improve their appearance and protect them from corrosion.
Quality Control: Quality checks are performed throughout the extrusion process to ensure the final products meet the required specifications for dimensions, strength, and surface finish.
Applications: Aluminum extrusions find applications in numerous industries, including construction (window frames, curtain walls, and structural components), automotive (bumpers, trim, and structural parts), aerospace (aircraft components), electronics (heat sinks), and consumer goods (frames, enclosures, and furniture).
Advantages: Aluminum extrusion offers several advantages, including its lightweight nature, high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, recyclability, and the ability to create complex shapes with tight tolerances.
Sustainability: Aluminum is a sustainable material because it is highly recyclable, and the energy required for recycling is significantly lower than for primary aluminum production.
How many types of aluminium extrusion methods
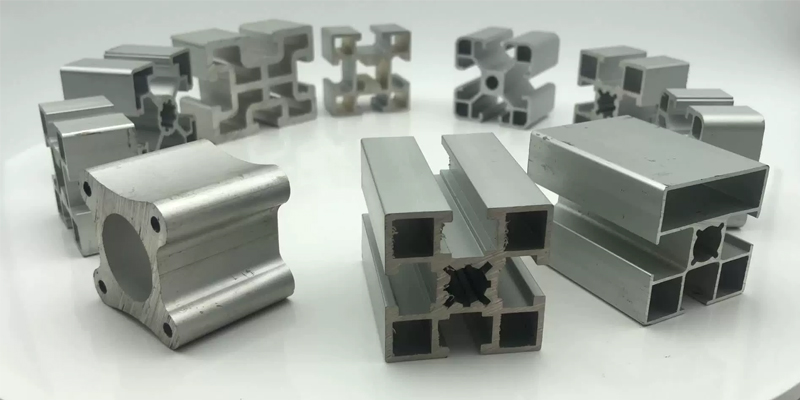
1. Hot Extrusion: In hot extrusion, the aluminum billet is heated to a temperature where it is easily deformable and then forced through a die to create the desired shape. This method is used for materials that require high deformation, like alloys with lower formability.
2. Cold Extrusion: Cold extrusion involves extruding aluminum at or near room temperature. This method is typically used for softer aluminum alloys and provides greater precision and surface finish compared to hot extrusion.
3. Direct Extrusion: In direct extrusion, the billet is placed in a stationary container, and a ram or piston applies pressure to force the billet through the die. This method is commonly used for simple shapes and profiles.
4. Indirect Extrusion: Indirect extrusion, also known as backward extrusion, involves a stationary die and a moving container (usually the billet) that is forced through the die. It is suitable for complex and intricate profiles.
5. Hydrostatic Extrusion: Hydrostatic extrusion uses a pressurized fluid to force the billet through the die. This method is primarily used for materials that are difficult to extrude using conventional methods.
6. Impact Extrusion: Impact extrusion is a cold extrusion process where the billet is placed in a die, and a punch impacts the billet to form the desired shape. This method is often used for creating small, cylindrical parts like cans.
7. Multi-Hollow Extrusion: This method involves extruding multiple hollow shapes simultaneously. It is used for creating profiles with multiple chambers, such as complex heat sinks.
8. Friction Stir Extrusion (FSE): FSE is a relatively newer extrusion technique that uses a rotating tool to join and extrude materials. It's used for joining and forming aluminum alloys with high strength and low melting points.
9. Spline Rolling Extrusion: This process uses rolling dies to create threads, splines, or other intricate shapes on the surface of extruded profiles. It's commonly used for making threaded aluminum rods or shafts.
10. Tubular Extrusion: Tubular extrusion involves creating hollow or tubular profiles by extruding aluminum through a die with a central void. This method is used for manufacturing aluminum tubing.
Different of these aluminium extrusion methods
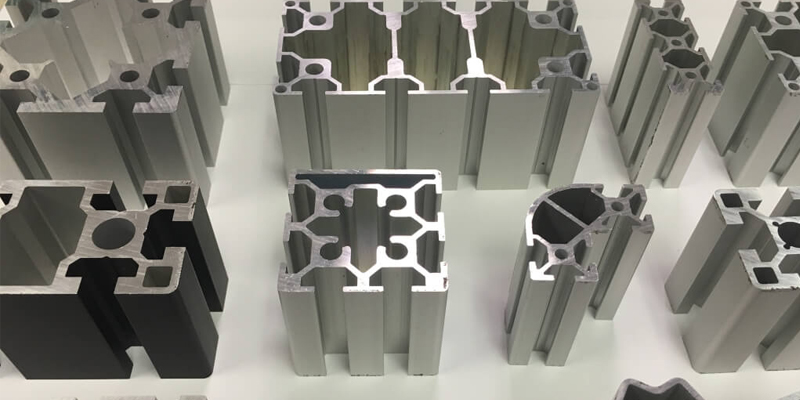
Hot Extrusion vs. Cold Extrusion:
Temperature: Hot extrusion involves heating the aluminum billet to a high temperature, while cold extrusion is done at or near room temperature.
Material Suitability: Hot extrusion is suitable for less ductile materials, while cold extrusion is better for softer aluminum alloys.
Surface Finish: Cold extrusion generally produces a smoother surface finish than hot extrusion.
Direct Extrusion vs. Indirect Extrusion:
Billet Movement: In direct extrusion, the billet is stationary, and the ram moves it through the die. In indirect extrusion, the billet is mobile, and the die remains stationary.
Complexity: Indirect extrusion is better suited for complex and intricate shapes, while direct extrusion is used for simpler profiles.
Hydrostatic Extrusion vs. Impact Extrusion:
Pressure Source: Hydrostatic extrusion uses a pressurized fluid, while impact extrusion employs a mechanical punch.
Applications: Hydrostatic extrusion is used for difficult-to-extrude materials, whereas impact extrusion is often used for small, cylindrical parts.
Multi-Hollow Extrusion vs. Friction Stir Extrusion (FSE):
Purpose: Multi-hollow extrusion creates profiles with multiple chambers, while FSE is primarily used for joining and forming aluminum alloys.
Method: Multi-hollow extrusion is a traditional extrusion process, while FSE involves a rotating tool.
Spline Rolling Extrusion vs. Tubular Extrusion:
Purpose: Spline rolling extrusion is used to create threads, splines, or other surface features, while tubular extrusion is for forming hollow or tubular profiles.
Die Design: Spline rolling uses rolling dies with specific profiles, whereas tubular extrusion uses dies with central voids.
Common applications for the above aluminium extrusion methods
Hot Extrusion:
Automotive Components: Hot extrusion is used to create automotive parts like cylinder heads, engine blocks, and transmission housings.
Aerospace Structures: Aircraft components, such as wing spars and structural elements, are often made using hot extrusion.
Railway Parts: Train frames, couplers, and other railway components are produced through hot extrusion.
Cold Extrusion:
Aluminum Cans: Cold extrusion is commonly used to manufacture aluminum beverage cans due to its precise forming capabilities.
Electrical Connectors: Cold extrusion is employed for producing electrical connectors and terminals with tight tolerances.
Hardware and Fasteners: Cold extrusion is used for making bolts, screws, and other small hardware items.
Direct Extrusion:
Simple Profiles: Direct extrusion is suitable for creating straightforward aluminum profiles like rods, bars, and simple shapes.
Window Frames: It is used for manufacturing standard aluminum window and door frames.
Indirect Extrusion:
Complex Profiles: Indirect extrusion is preferred for producing intricate aluminum profiles, such as heat sinks, decorative trim, and custom shapes.
Automotive Trim: Indirect extrusion is used for making various automotive trim components.
Hydrostatic Extrusion:
High-Strength Components: Hydrostatic extrusion is used to create high-strength aluminum components, including military and aerospace parts.
Oil and Gas Industry: Some specialized components for the oil and gas industry are produced using this method.
Impact Extrusion:
Aluminum Cans: Impact extrusion is commonly employed for manufacturing aluminum beverage cans.
Cosmetic Packaging: It is used for producing aluminum containers for cosmetics and pharmaceuticals.
Multi-Hollow Extrusion:
Heat Exchangers: Multi-hollow extrusion is used to create complex heat exchanger profiles with multiple chambers.
Electronic Enclosures: It is employed for making enclosures with integrated cooling channels for electronics.
Friction Stir Extrusion (FSE):
Welded Aluminum Components: FSE is used for joining and forming aluminum alloys with high strength, making it suitable for aerospace and automotive applications.
Railway Carriages: FSE can be used for producing lightweight, high-strength components in railway carriage manufacturing.
Spline Rolling Extrusion:
Threaded Components: Spline rolling extrusion is used to create threaded aluminum rods, shafts, and other components.
Automotive Axles: It is employed in the production of automotive axle shafts.
Tubular Extrusion:
Aluminum Tubing: Tubular extrusion is the primary method for manufacturing aluminum tubing used in various industries, including construction and automotive.
Piping and Conduit: It is used to create aluminum pipes and conduits for plumbing and electrical applications.
Materials of these aluminium extrusion methods
Hot Extrusion:
Aluminum Alloys: Hot extrusion can be used with a wide range of aluminum alloys, including 1000, 2000, 6000, and 7000 series alloys.
Applications: Hot extrusion is often employed for producing components in the aerospace, automotive, and railway industries, where high-strength and heat-resistant alloys may be used.
Cold Extrusion:
Soft Aluminum Alloys: Cold extrusion is typically used with softer aluminum alloys like 1000 and 3000 series.
Applications: Common applications include aluminum cans, electrical connectors, and hardware.
Direct Extrusion:
Aluminum Alloys: Direct extrusion is suitable for a wide range of aluminum alloys, depending on the specific profile requirements.
Applications: It is used for simple profiles like rods, bars, and basic shapes.
Indirect Extrusion:
Aluminum Alloys: Indirect extrusion can be used with various aluminum alloys, including those suitable for complex shapes.
Applications: Complex profiles, automotive trim, and decorative components can be produced using this method.
Hydrostatic Extrusion:
High-Strength Aluminum Alloys: Hydrostatic extrusion is often applied to high-strength aluminum alloys such as 7000 series.
Applications: Aerospace components, military hardware, and specialized parts benefit from the strength of these alloys.
Impact Extrusion:
Soft to Medium Strength Aluminum Alloys: Impact extrusion is typically used with softer to medium-strength aluminum alloys like 1000 and 3000 series.
Applications: Aluminum beverage cans and small cylindrical parts are common products produced via impact extrusion.
Multi-Hollow Extrusion:
Aluminum Alloys: Multi-hollow extrusion can be used with a variety of aluminum alloys, depending on the desired properties of the final product.
Applications: Heat exchangers, electronic enclosures, and complex profiles with multiple chambers are typical applications.
Friction Stir Extrusion (FSE):
High-Strength Aluminum Alloys: FSE is suitable for high-strength aluminum alloys such as 2000 and 7000 series.
Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, and other applications where high-strength and lightweight properties are required.
Spline Rolling Extrusion:
Aluminum Alloys: Spline rolling extrusion can be applied to various aluminum alloys based on the desired thread or spline specifications.
Applications: Threaded aluminum rods, shafts, and components used in automotive and machinery are common products.
Tubular Extrusion:
Aluminum Alloys: Tubular extrusion can be used with a range of aluminum alloys depending on the intended use.
Applications: Aluminum tubing for construction, automotive, and various industries, as well as piping and conduit, are produced using this method.
The specific alloy chosen for extrusion depends on factors like strength, corrosion resistance, formability, and the intended application's requirements.