Creating a solid understanding of rapid prototyping is crucial for product managers navigating the dynamic landscape of product development. Rapid prototyping, a key agile strategy, streamlines the process by swiftly producing 3-dimensional prototypes for testing and validation throughout the development cycle. This approach involves creating realistic simulations of a product or feature, allowing for optimization in terms of shape, size, and usability.
① What is Rapid Prototyping?
Rapid prototyping serves as a strategic cornerstone in the product development journey. It involves the agile creation of 3-dimensional prototypes for products or features, enabling efficient testing and optimization of key characteristics such as shape, size, and overall usability.
② Prototyping in Action: How Does it Work?
Prototyping is a vital step in validating the hypothesis that a product effectively addresses its intended problem. While not fully functional, prototypes offer a realistic appearance that allows potential users to interact and provide valuable feedback.
The rapid aspect comes into play with the speed of prototype production, feedback gathering, and subsequent iterations. Teams must strike a balance between creating a prototype authentic enough for genuine user reactions and avoiding excessive resource expenditure.
③ Techniques in Rapid Prototyping
To gather authentic prototype feedback, it's crucial to create high-fidelity prototypes that closely resemble the final product. This involves thorough consideration of use cases and leveraging real software development and UX expertise.
Wireframing and clickable sites serve as intermediate options for when fully visualized prototypes are premature or costly. These techniques allow for quicker feedback on various elements of the solution.
④ Why Product Managers Need to Grasp Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping empowers product managers to fast-track real-world customer feedback, saving valuable development resources. It transforms hypotheses into tangible tests with actual users, providing insights into user needs and significantly shortening time to market.
The iterative nature of rapid prototyping demands active collaboration and responsiveness from product teams. This ensures quick analysis of feedback and informed decisions on subsequent iterations or full product development.
⑤ Conclusion: Unlocking Efficiency in Product Development
Rapid prototyping emerges as a time-saving and risk-mitigating tool for product teams. The qualitative validation obtained from user interactions with prototypes reduces the risk of final products failing to meet expectations.
The externalized thinking fostered by rapid prototyping breaks down communication barriers, ensuring alignment between product vision and development outcomes. This streamlined process leads to delivering a top-tier product to customers and prospects.
Rapid prototyping stands as a cornerstone in modern product development, offering a proactive approach to validate assumptions and deliver products that resonate with user needs.
⑥ What are the rapid prototyping methods in GD-HUB?
3D Printing: Utilizing additive manufacturing to create physical prototypes layer by layer. This method is particularly effective for testing the form and structure of a product.
Stereolithography (SLA):This additive manufacturing technique uses UV light to solidify liquid resin layer by layer, producing high-resolution prototypes with smooth surfaces.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): FDM builds prototypes by extruding layers of thermoplastic material. It's widely used for creating functional prototypes quickly.
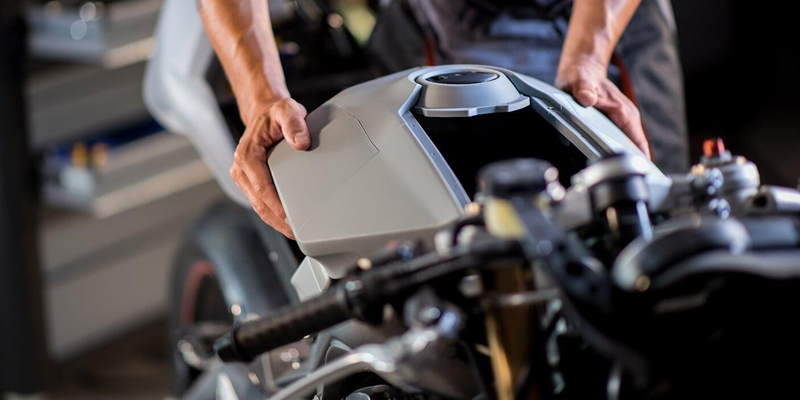

Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): SLS uses a laser to sinter powdered material, typically nylon or polyamide, layer by layer. It's suitable for creating durable and functional prototypes.
CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control machining is used to create prototypes by removing material from a block. It's a precise method suitable for testing functional components.
Injection Molding:This method involves injecting molten material into a mold to create prototypes that closely resemble the final product. It's beneficial for assessing mass production viability.
Vacuum Casting: This method involves creating a silicone mold from a master pattern and then casting materials like polyurethane into the mold to produce multiple replicas.
Sheet Metal Fabrication: Ideal for products involving metal sheets, this method cuts, bends, and assembles metal sheets to create functional prototypes.
Rapid Tooling: Creating prototype molds quickly to assess mass production feasibility. It's often used in conjunction with injection molding.
Each method has its strengths and is chosen based on the specific requirements of the project, including materials, precision, and the intended purpose of the prototype. The choice of method depends on factors such as the complexity of the design, desired prototype fidelity, and the materials involved in the final product.
Discover the efficiency gains from rapid prototyping.