Introduction
Low Pressure Injection Moulding (LPIM) represents a significant advancement in the field of manufacturing, offering a versatile and efficient approach to producing high-quality parts. This article provides an in-depth look at LPIM, exploring its processes, benefits, applications, and how it compares to traditional high-pressure injection moulding methods.
What is Low Pressure Injection Moulding?
Low Pressure Injection Moulding is a process that involves injecting molten materials into a mould at lower pressures than traditional injection moulding. This method typically uses polyamide or polyolefin-based materials, which are known for their excellent electrical and thermal properties. The low-pressure process reduces stress on the mould, allowing for the production of more intricate designs and the use of less robust, cost-effective mould materials.
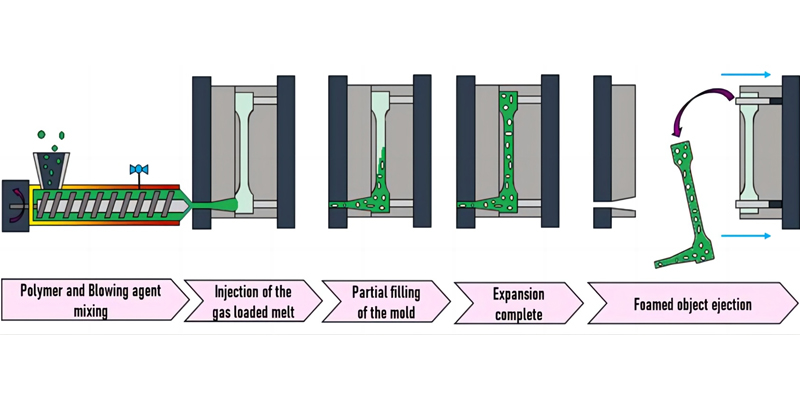
The LPIM Process
The LPIM process can be broken down into several key steps:
Material Preparation: The chosen material, often in the form of granules, is melted into a liquid state.
Injection into the Mould: The molten material is injected into a mould at low pressure.
Cooling and Solidification: Once in the mould, the material cools and solidifies into the desired shape.
Ejection: The finished part is ejected from the mould, ready for use or further processing.
Advantages of Low Pressure Injection Moulding
LPIM offers numerous benefits:
Reduced Stress on Moulds: Lower pressure means less wear and tear on moulds, extending their lifespan.
Complex Part Design: It allows for the creation of complex parts with intricate geometries.
Cost-Effective: The process can use cheaper mould materials, reducing overall production costs.
High Material Compatibility: LPIM is compatible with a wide range of materials, including thermally sensitive substrates.
Eco-Friendly: The process can be more environmentally friendly, as it often uses recyclable materials and generates less waste.
Here is a table comparing the advantages of Low Pressure Injection Moulding (LPIM) and traditional High Pressure Injection Moulding (HPIM):
Factor | Low Pressure Injection Moulding (LPIM) | High Pressure Injection Moulding (HPIM) |
Tooling Cost and Durability | Lower tooling costs due to less wear and tear on molds; molds can be made of less expensive materials. | Higher tooling costs; molds must be stronger and more durable to withstand high pressure, leading to higher costs. |
Part Stress | Lower injection pressures mean less internal stress in molded parts, ideal for delicate or sensitive components. | Higher injection pressures can induce more internal stress in parts, which may require additional processing to relieve. |
Cycle Time | Longer cycle times due to lower pressure and slower cooling. | Shorter cycle times due to high pressure and faster cooling, increasing production efficiency. |
Part Design Flexibility | Better for encapsulating delicate parts or electronics without damage; can mold around inserts and cables without harming them. | Less suitable for encapsulating delicate parts; high pressure can damage sensitive components or electronic inserts. |
Material Range | Limited to materials that can flow under low pressure; typically used with thermoplastics and some elastomers. | Broader range of materials, including high-strength, engineering-grade thermoplastics. |
Surface Finish and Detail | Surface finish may not be as fine or detailed due to lower pressure. | Higher pressure allows for better surface finish and more intricate details. |
Part Strength and Tolerance | Lower mechanical strength compared to high-pressure counterparts; tolerances might not be as tight. | Parts generally have higher mechanical strength and can be engineered to meet tighter tolerances. |
Applications | Ideal for overmolding, encapsulation of electronics, and parts where internal stress must be minimized. | Suited for a wide range of applications, especially where high strength, precision, and volume production are required. |
Environmental Impact | Potentially lower energy consumption due to lower pressures. | Higher energy consumption due to high pressures and temperatures. |
Both LPIM and HPIM have their unique advantages, and the choice between them depends on the specific requirements of the project, including the nature of the parts being produced, material considerations, cost factors, and desired production volume and efficiency.
Applications of LPIM
LPIM is used in various industries, including:
Electronics: For encapsulating and protecting electronic components.
Automotive: In the production of lightweight, complex parts.
Medical Devices: Due to its precision and material compatibility, it's ideal for medical device manufacturing.
Comparison with High-Pressure Injection Moulding
While traditional high-pressure injection moulding is faster and suitable for producing large volumes of simple parts, LPIM is better suited for complex, delicate components, especially where there is a need for reduced stress on materials.
Low Pressure Injection Moulding (LPIM) is a versatile manufacturing process used in various industries. Below is a table outlining the applications of LPIM in different industries:
Industry | Applications of LPIM |
Electronics | Encapsulation of electronic components, cable harnesses |
Automotive | Wire harnesses, connectors, sensor housings |
Medical | Medical device components, protective casings |
Consumer Goods | Overmolding on electronics, wearable devices |
Telecommunications | Enclosures for communication devices, connectors |
Aerospace | Low-stress components, wire harnesses, sensor housings |
Industrial | Seals, gaskets, protective components for machinery |
Energy | Solar panel components, insulators, connectors |
Defense | Encapsulation of sensitive components, cable harnesses |
Marine | Waterproof enclosures, cable seals, connector housings |
LPIM is particularly useful for encapsulating and protecting sensitive components in environments where traditional high-pressure injection moulding might damage the components. It's ideal for producing parts with complex geometries and can be used with a wide range of materials, including thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers.
Conclusion
Low Pressure Injection Moulding is a valuable process in modern manufacturing, offering versatility, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to produce complex parts with minimal stress. As industries continue to evolve, the demand for innovative manufacturing methods like LPIM is likely to grow, making it a key area of interest for manufacturers seeking to stay ahead in a competitive market.
With cutting-edge technology and a team of experienced professionals, GD-HUB specializes in delivering precision LPIM solutions tailored to your specific needs. Whether it's encapsulating delicate electronic components, creating custom overmoldings, or producing intricate parts with minimal internal stress, GD-HUB's LPIM services stand out in the industry.
Choose GD-HUB for Expert LPIM Services, You Can Get:
Leverage the benefits of LPIM for your specialized projects.
Experience precision and quality with every part.
Collaborate with a team skilled in advanced LPIM techniques.
Discuss your project requirements and specifications.
Explore innovative LPIM solutions for diverse applications.
Receive expert advice and comprehensive support.
Ensure high-quality results with a focus on precision and customization.
Take advantage of GD-HUB’s extensive experience across various industries.
Make the move towards advanced manufacturing solutions.