Chromate coatings, known by various names like Alodine®, yellow Bonderite®, Iridite®, and chem film, play a crucial role in enhancing the durability and functionality of metals such as aluminum, cadmium, copper, magnesium, steel, tin alloys, and zinc. In GD HUB Precision Technology Co., Limited, we specialize in applying these coatings predominantly to aluminum alloys, tailoring the finish based on the metal’s purity and surface texture.
Diving into Chromate Coatings
Essence of Chromate Conversion Coating:
Chromate conversion coating is more than just a surface treatment. It's a chemical process that bonds a chromic-acid-based compound to the metal, significantly improving the metal’s resistance to electrical conductivity and corrosion. This process differs fundamentally from plating, as it forms a film that integrates both physically and chemically with the metal.
Visual Diversity of Chromate Coated Parts:
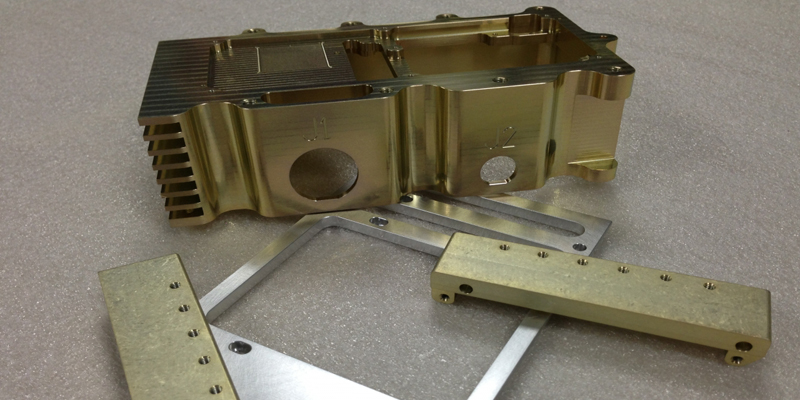
The chromate process can yield a spectrum of colors, primarily an iridescent greenish-yellow on lighter metals. However, the final appearance can vary across different metal alloys. For instance, treating ten distinct alloys with the same chromate process can result in ten unique color shades, especially in cast aluminum alloys, where color variations can be particularly striking.
Alloy Type | Expected Color After Chromate Treatment |
Pure Aluminum | Light Yellow to Golden |
Aluminum Alloy (High Purity) | Slight Iridescent, Pale Yellow |
Aluminum Alloy (Low Purity) | Darker Yellow, sometimes Brownish |
Aluminum Alloy (Cast) | Wide Range: Pale Yellow to Deep Golden or Brown |
Zinc | Bright Yellow to Greenish-Yellow |
Magnesium Alloy | Light Yellow to Greenish Tint |
Steel | Gray to Black (if applicable) |
Tin Alloy | Light Yellow, might have Greenish Tint |
Copper | Golden Yellow to Brownish Yellow |
Cadmium | Bright Yellow, sometimes with Orange Hue |
*Typical Observations of Chromate Treatments of Common Alloys Generic Table
Standards and Compliance in Chromate Coating
Military Standards in Chromate Application:
We adhere to military standards, specifically MIL-C-5541 and MIL-DTL-5541, for most of our parts. While these standards are essentially the same, they often create confusion due to their different terminologies.
RoHS Compliance and Chromate Coating:
In compliance with RoHS standards, chromate coatings must be clear. This means that parts traditionally coated in yellow will now be clear if they need to be RoHS compliant. So, if your parts arrive without the expected yellow hue, they are still coated, but with a clear, compliant compound.
*What is the RoHS standard? and the RoHS standard for chromates?
The RoHS standard, which stands for "Restriction of Hazardous Substances," is a directive initially implemented by the European Union. It's designed to limit the use of specific hazardous materials found in electrical and electronic products. The purpose of RoHS is to reduce the environmental impact and health hazards caused by these materials.
Key Elements of RoHS Standard:
Restricted Substances: RoHS restricts the use of six hazardous materials in the manufacture of various types of electronic and electrical equipment. These substances are Lead (Pb), Mercury (Hg), Cadmium (Cd), Hexavalent Chromium (Cr(VI)), Polybrominated Biphenyls (PBB), and Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDE).
Product Scope: It applies to a wide range of electronic equipment, including but not limited to household appliances, IT and telecommunication equipment, lighting, electrical and electronic tools, toys, and sports equipment.
Compliance and Certification: Manufacturers need to ensure their products, and the components within them, comply with RoHS standards. This often involves certification and testing to demonstrate compliance.
RoHS Standard for Chromates:
In the context of chromates, the RoHS standard specifically pertains to the restriction of Hexavalent Chromium (Cr(VI)). Hexavalent Chromium is a toxic form of chromium that is hazardous to both human health and the environment.
Restriction in Coatings: For chromate conversion coatings, the use of hexavalent chromium is a major concern. These coatings are commonly used for corrosion protection and as a primer to improve the adhesion of paints on metals like aluminum, zinc, and their alloys.
RoHS-Compliant Chromate Coatings: In response to RoHS regulations, the industry has developed alternative chromate treatments that do not use hexavalent chromium. These are often referred to as RoHS-compliant chromates. They typically result in a clear or bluish tint, as opposed to the traditional yellow or greenish-yellow color associated with hexavalent chromium-containing coatings.
Impact on Industry: The shift to RoHS-compliant chromate coatings has been significant, especially for industries that rely heavily on metal parts and components, such as electronics, automotive, aerospace, and defense.
The RoHS standard plays a crucial role in limiting the use of hazardous substances in electronic products, including restricting the use of hexavalent chromium in chromate coatings. The adoption of RoHS-compliant chromate coatings is part of the broader effort to make electronic products safer and more environmentally friendly.
The Surprising Reality of Yellow Chromate
Color Variations in Yellow Chromate:
Contrary to what its name might suggest, yellow chromate doesn’t always manifest in yellow. The hues can range from light yellow to golden brown. This variation is due to the acid process used in chromating, which can leave subtle etch marks and color variations from batch to batch.
Chromate Coating: Beyond Aesthetics
Commercial Purpose Over Cosmetic Appeal:
Chromate coatings are designed for industrial applications rather than for decorative purposes. If your project requires a specific aesthetic finish, we’re here to guide you to the right choice that aligns with your objectives.
Choosing the Suitable Chromate Coating
Tailoring Chromate Treatment for Your Needs:
Our expertise extends to helping you select the perfect chromate treatment for your parts. If RoHS compliance is a requirement, a clear Class 2 chromate is necessary. For other applications, you might choose between clear Class 1A, ideal as a paint primer, or yellow Class 3 for enhanced corrosion resistance.
Quick Reference for Chromate Coating Specifications
GD HUB Precision Technology Co., Limited's Chromate Guide:
MIL-C-5541 and MIL-DTL-5541: Type 1, Class 1A (always yellow) or Class 3 (yellow or clear).
MIL-DTL-5541: Type 2, Class 1A or 3 (always clear and RoHS compliant).
Partner with GD HUB Precision Technology Co., Limited
For top-tier metal fabrication and chromate conversion coating, our expertise and commitment to quality make us your ideal partner. Contact us for a quote and let us enhance your metal parts with our specialized chromate coating services.